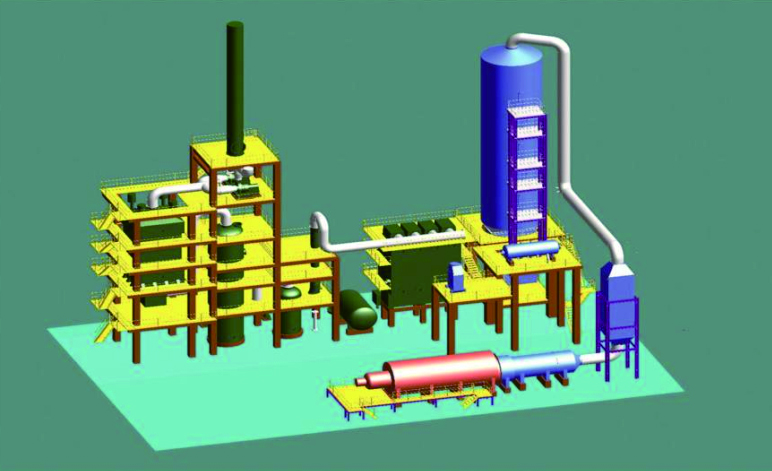
WSA
H2S-containing sour gas first enters the furnace, where SO2-containing high-temperature furnave gas is generated,which the passes through the waste heat boiler to recover the heat for generation of steam before going into the converter. The converter is divided into two or three stages, with superheater or steam generator provided between the stages as inter-coolers. In the converter, SO2 is converted to SO3, which is then cooled in the gas cooler before going to the sulphuric acid condenser, where SO3 is cooled and hydrolyzed with water to from sulphuric acid, and then condensed into 97-98% concentrated sulphuric acid. The condenser will use tube-and-shell falling film condenser, where SO3 will flow upwards, while condensed concentrated sulphuric acid will flow downwards. 97-98% concentrated sulphuric acid leaving the bottom of the sulphuric acid condenser will the go through the sulphuric acid cooler before going to the sulphuric acid storage tanks.
Cooling air first enters the shell side of the sulphuric acid condenser to cool the SO3, hot air will go into the burner for burning, while excess hot air will be mixed with tail gas leaving from the top of the condenser for venting via the stack.
The evaporator and superheater in the converter, and the waste heat boiler and steam drum together form a heat recovery system to generate steam.